A clinical trial of Actiphage, a promising new diagnostic for tuberculosis infection, has shown for the first time that live...
Phage-based diagnostics
Phage-based detection assays benefits from the selectivity of a phage for a specific bacterial target.
Loading...
Phage-based diagnostics identify bacterial infections by detecting live pathogens circulating in the blood.
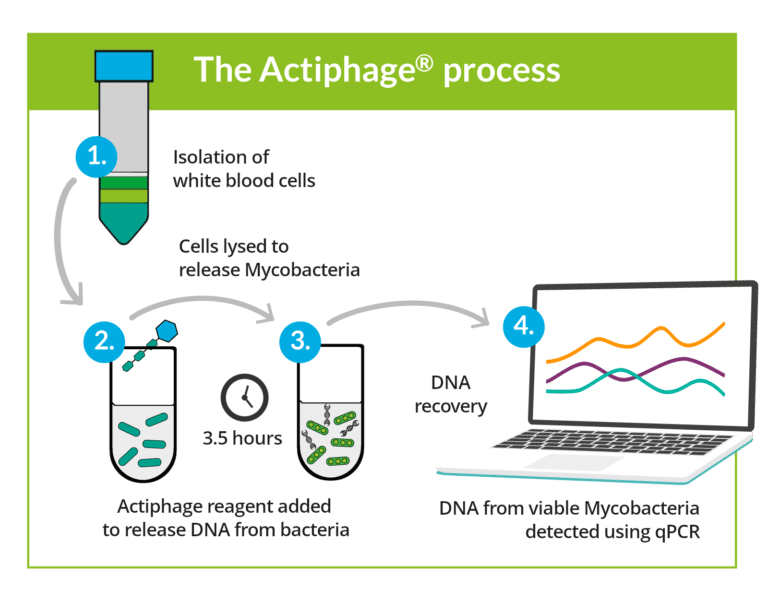
A phage is a virus-like particle that is specific to a particular stain of bacteria, such as Mycobacteria Tuberculosis (Mtb) that causes tuberculosis (TB). Actiphage takes advantage of the specificity of interaction between a phage and its host bacteria to create a rapid diagnostic for TB and other diseases caused by mycobacteria.
The phage is used to find live mycobacteria; it penetrates the bacteria, replicating rapidly within it. As the volume inside increases, eventually the tough cell walls will rupture, releasing the bacterial DNA (lysing the bacteria).
The DNA is then available for identification with qPCR.
The benefits of phage-based diagnostics are significant:
Identifies live infection at an early stage - the phage only replicates in live cells and is able to detect its host bacteria at very low levels in the blood (bacteraemia), before the infected person or animal begins to generate an immune response.
Rapid diagnostic - the bacterial DNA is released within hours to enable rapid identification with qPCR.
Identifies the genotype of the mycobacteria - There are many different strains of mycobacteria, and some genotypes are more virulent than others. With Actiphage as a companion diagnostic it would be possible to provide personalised medicine, matching the drug to the strain.
Provides screening of high risk populations - children, those with HIV or diabetes and those malnourished or stressed are more likely to develop TB disease but also find it difficult to produce sputum for analysis. Actiphage is a blood test that can be produces samples that are easy to handle in the community.
The results from initial trials are very promising.
Researchers at Leicester Respiratory NIHR Biomedical Centre (2022) used Actiphage to screen high risk patients.
It was the first study to successfully isolate Mtb in the blood and to use this to distinguish between latent TBI and incipient TBI.
Showed bacteraemia (bacteria in the blood) can be used to provide early-stage diagnosis.
Demonstrated that Actiphage had potential for rapid blood test for screening vulnerable populations.
The research was presented at the 32nd European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases
Related content
Loading...
February 29, 2024
Phage-based diagnostics combined with qPCR offer a highly specific and sensitive approach to developing pathogen-directed markers of TB, says Dr Pranabashis Haldar in a new article.
Phage-based diagnostics combined with qPCR offer a highly specific and sensitive approach to developing pathogen-directed markers of TB, says Dr...
November 21, 2022
The Global Plan to End TB is a costed public health plan. It aims to cut deaths by 90% in 8 years. A key recommendation of the report is to universally replace sputum microscopy with rapid molecular diagnostics.
November 21, 2022
The Global Plan to End TB is a costed public health plan. It aims to cut deaths by 90% in...
November 14, 2022
For some of the world's most infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis (TB), The WHO has developed target product profiles (TPPs) to assist developers of new diagnostics.
November 14, 2022
For some of the world's most infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis (TB), The WHO has developed target product profiles (TPPs)...
November 14, 2022
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that is spread by inhaling tiny droplets in the air released when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Many people carry the disease without realising, creating a reservoir of disease in a population.
November 14, 2022
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that is spread by inhaling tiny droplets in the air released when an infected...